- เราเริ่มรู้จักหนังสือเล่มนี้ครั้งแรกตอนฟัง Huberman Lab Podcast: Understanding & Treating Addiction (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p3JLaF_4Tz8) ที่ Dr. Anna Lembke มาออกรายการ แต่ตอนนั้นยังไม่ได้คิดจะซื้อมาอ่าน แล้วมาได้ยินตอนที่คุณ รวิส Mission to the moon พูดถึงอีกที จึงได้ถือโอกาสลองซื้อมาอ่าน
- โดย ส่วนตัวมีความสนใจในด้าน Human body & brain mechanism อยู่แล้ว ยิ่งเราทำงานอยู่ในด้าน AI, Computer Science ยิ่งที่ทำให้เชื่อว่าจริง ๆ แล้วคนเรามี mechanism บางอย่างที่ drive เราอยู่ข้างหลัง
- มี quoute หนึ่งที่เคยได้ยินจำไม่ได้ว่าได้ยินจาก huberman lab หรือ ในหนังสือ (อาจจะจำมาผิดได้)
Dopamine is a single universal currency in human life
- เพราะว่าทุกอย่าง action, experience, achievement, money, … จะถูก track กลับมาที่ Chemical in the brain -> How we feel
- ซึ่งช่วงนี้จะได้ยิน Concept First Principle บ่อยๆ เราคิดว่า Dopamine, Chemical in the brain นี่น่าจะเป็น First principle ของมนุษย์ไม่ทางใดก็ทางหนึ่ง
- อันนี้เกริ่นความเห็นส่วนตัวไปเยอะแล้ว กลับมาที่ เนื้อหาที่น่าสนใจของหนังสือเล่มนี้ดีกว่า
Dopamine
- Dopamine เป็นสารสื่อประสาทชนิดหนึ่ง ทำหน้าที่เกี่ยวกับ reward processing, motivation
- ภาพตัวอย่าง NEUROTRANSMITTER
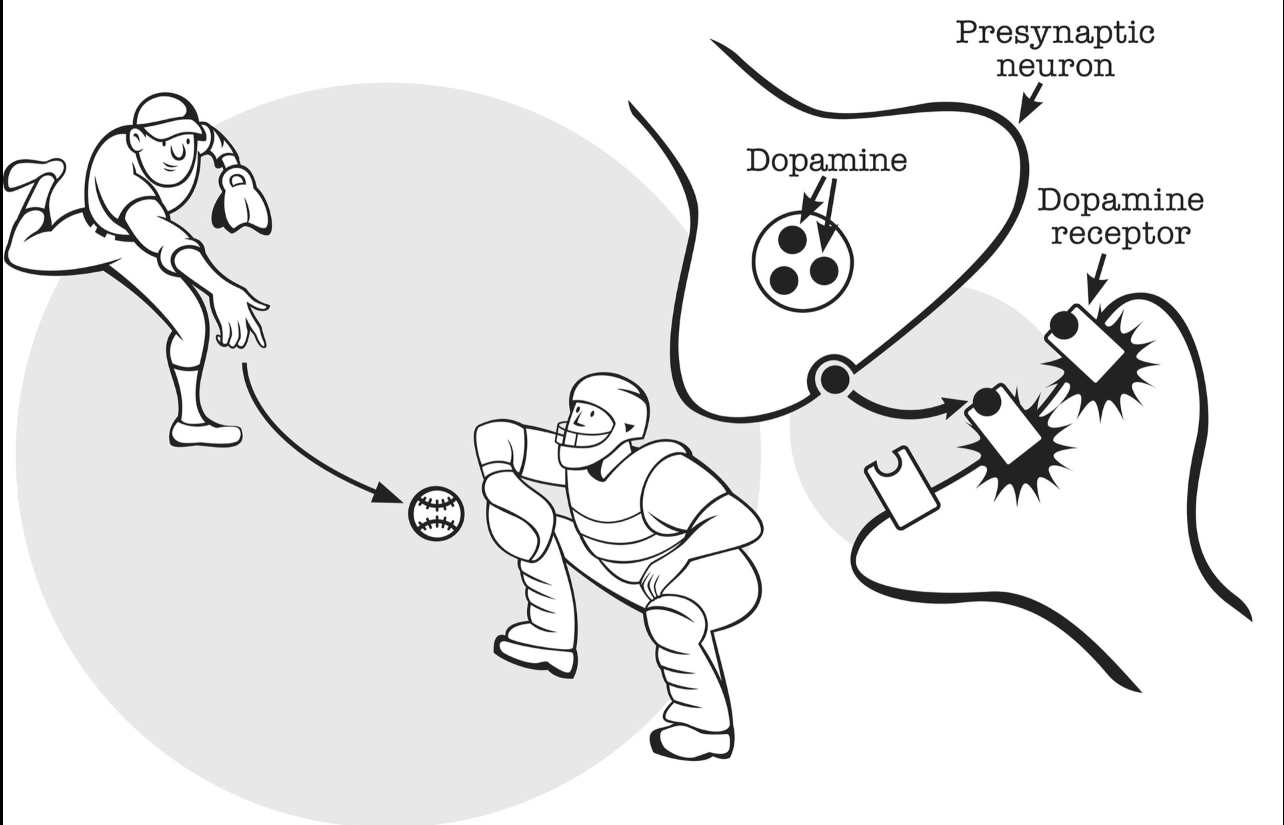
- Quote ข้างล่างนี้อาจจะเป็นตัวที่อธิบายว่าทำไม Capitalism ถึง work (Drive by Wanting)
Dopamine may play a bigger role in the motivation to get a reward than the pleasure it self. Wanting more liking.
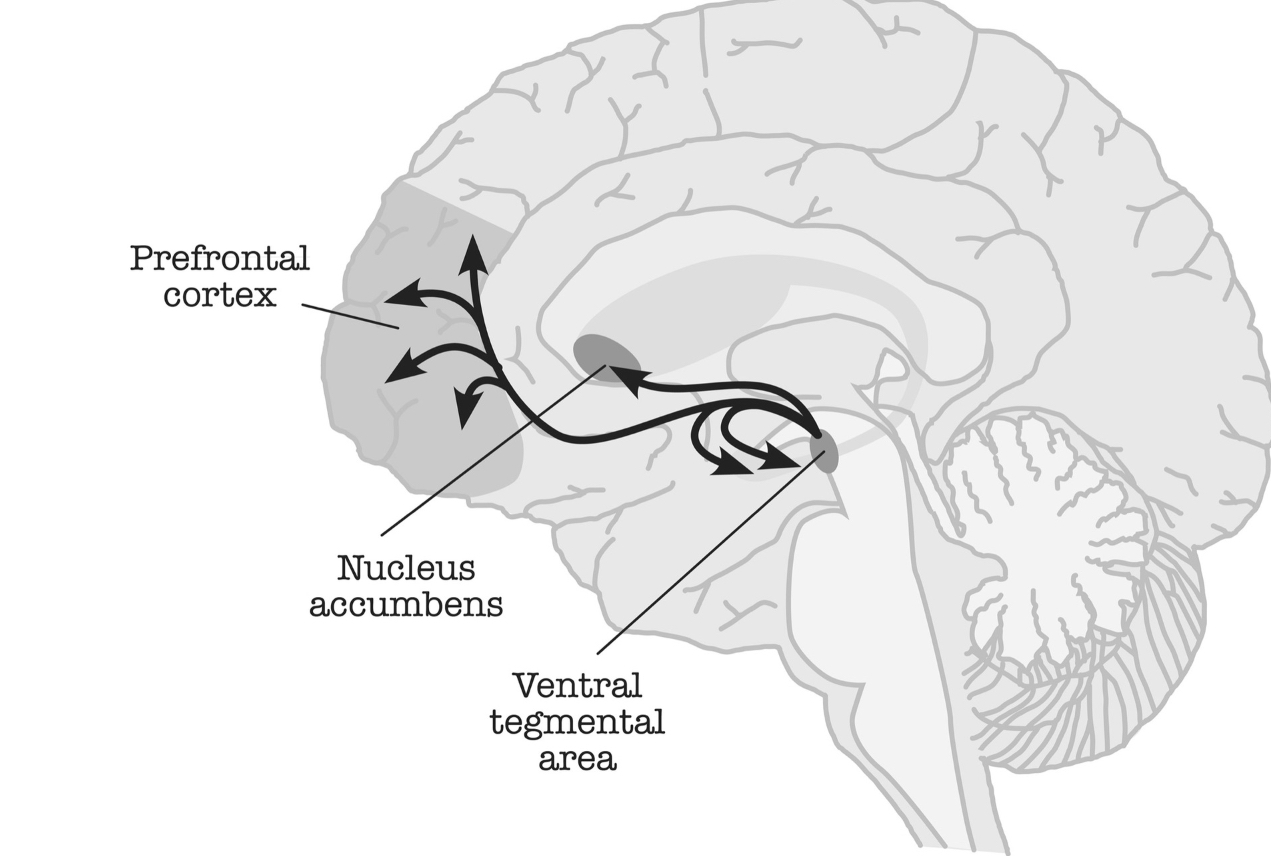
Dopamine Pathway
- Flow การไหลของ Dopamine เวลาถูกกระตุ้น
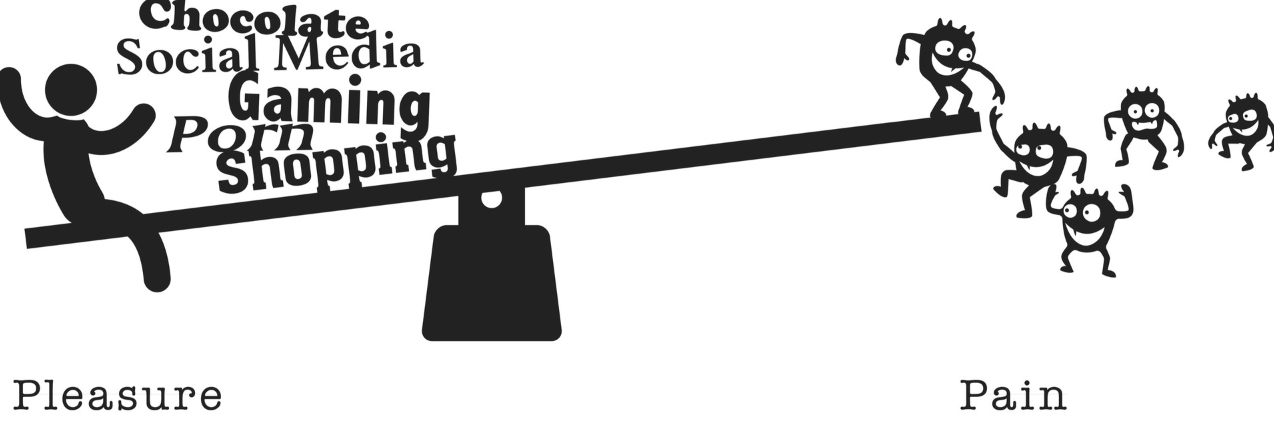
Pleasure & Pain
The brain processes pleasure and pain in the same place. Further, pleasure and pain work like opposite sides of a balance.
- ส่วนตัวคิดว่า concept นี้น่าสนใจที่สุดละ เขาบอกว่า pain & pleasure เป็นเหมือน ไม้กระดานที่ pain และ pleasure ที่อยู่คนละฝั่งกันสิ่งที่เราต้องทำคือพยายาม balance ทั้ง 2 ฝั่ง ซึ่งทั้ง 2 ฝั่ง จะ relate กัน เวลาฝั่งนั้นขึ้น สุดท้ายระบบจะค่อยๆปรับสมดุลกลับมาให้ balance
What goes up must come down
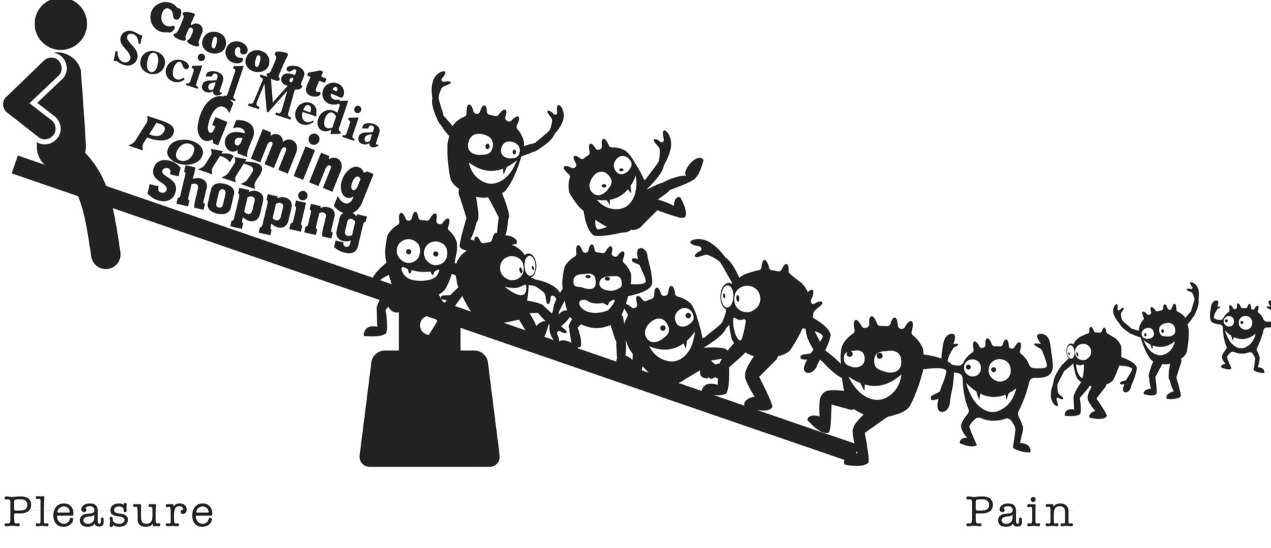
- การที่เราทำ pleasure stimulus เดิม ซ้ำๆ จะทำให้เรา pleasure กับสิ่งนั้นน้อยลงและต้องใช้มันมากขึ้นถึงจะได้ pleasure เท่าเดิม
With repeated exposure to the same or similar pleasure stimulus, the initial deviation to the side of pleasure gets weaker and shorter and the after-response to the side of pain gets stronger and longer, a process scientist call neuroadaptation. That is, with repetition, our gremlins get bigger, faster and more numerous and we need more of our drug of choice to get the same effect.

Addictions
One of the biggest risk factors for getting addicted to any drug is easy access to that drug. When it's easier to get a drug, we're more likely to try it. In trying it, we're more likely to get addicted to it.
- ในหนังสือเล่มนี้ไม่ได้บอกไว้ว่าจริงๆแล้วนิยาม ของ addictions คืออะไร
- แต่ถ้าเราที่หาในเน็ต คือ chronic relapsing disorder (การติดเรื้อรัง)
Recovery
- หัวข้อนี่ยังไม่ค่อยแน่ใจ ในหนังสือก็มียกตัวอย่าง คนที่สามารถ recovery from addict ได้ แต่ เหมือนใน podcast ก็มีเคสที่ไม่สามารถ recovery from addict ได้
- คิดว่าถ้าอยากเข้าใจต้อง take time หาข้อมูลต่อ
What can we take benefit from this book ?
- use wanting to get reward drive action when unmotivated
- try to balance pleasure & pain, not seeking heavily only pleasure
- Q: How scientist measure Dopamine
- Q: In the future can we simplify Dopamine measurement and use it in many use-cases.